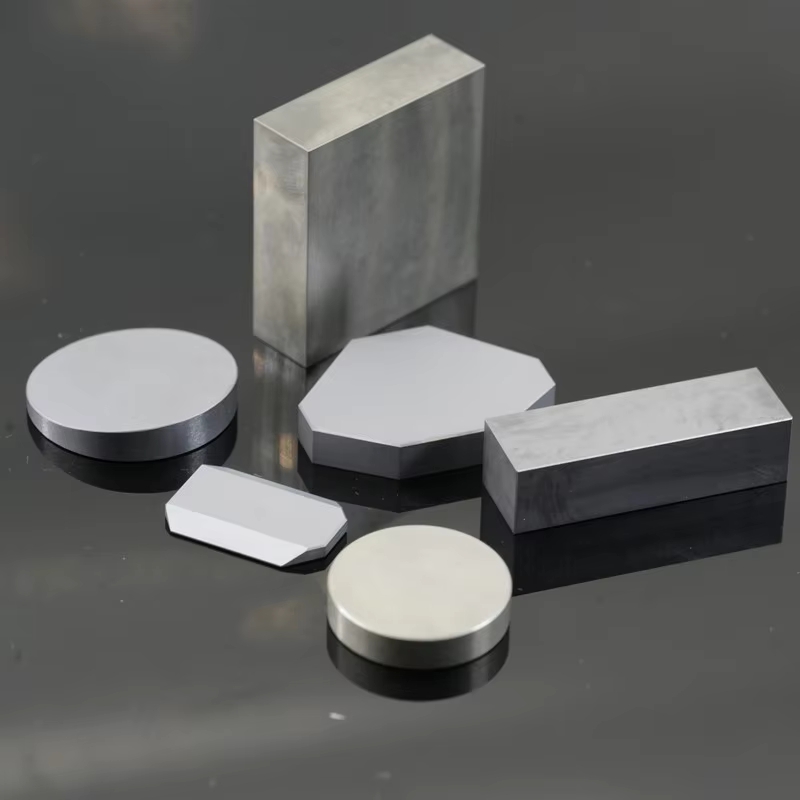
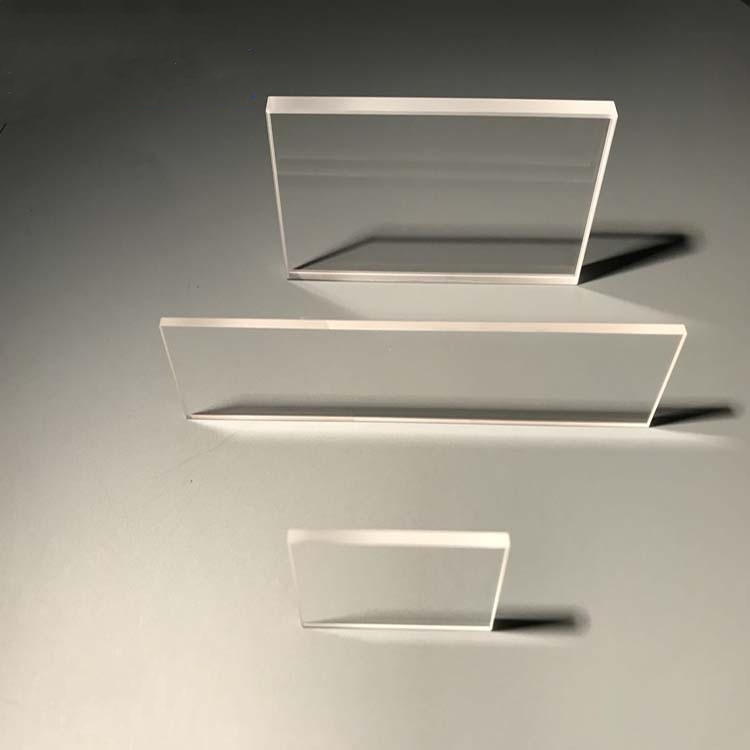
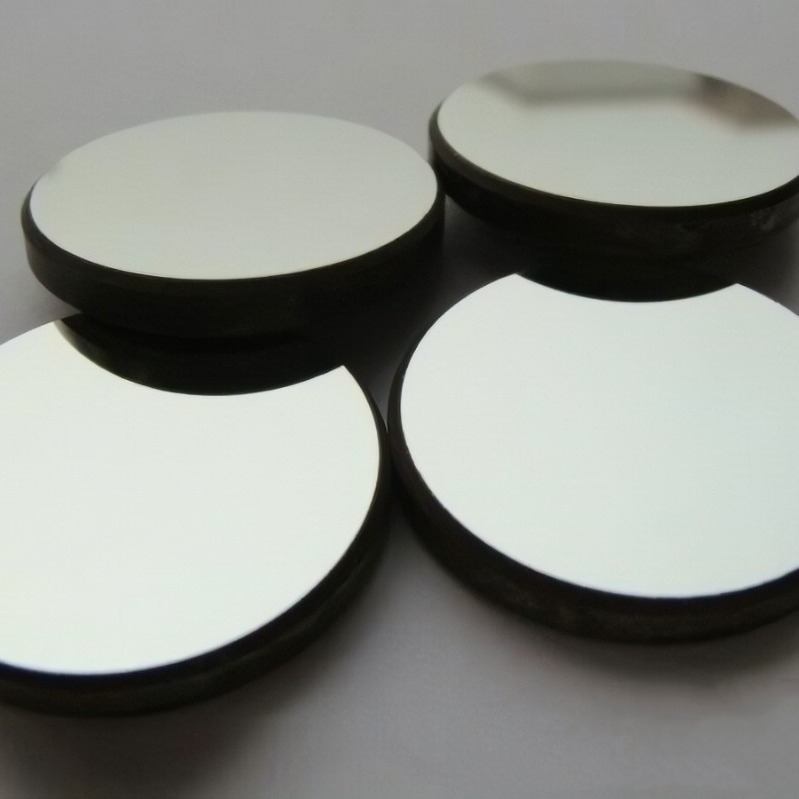
Zone-melted silicon (FZ silicon) is a high-purity semiconductor material produced using the float-zone refining process, ensuring minimal impurities and superior crystallographic uniformity. It offers excellent electrical conductivity, strong thermal stability, and optimized optical properties, making it ideal for semiconductor fabrication, photonics, power electronics, and high-precision scientific applications. Its refined structure enables enhanced charge carrier mobility and reliable performance in demanding technological environments.
Product Overview:
Zone-melted silicon (FZ silicon) is a high-purity single-crystal silicon material produced using the zone melting technique. This method results in silicon with very low impurity content and excellent optical properties. Due to its high transmission, low optical absorption coefficient, and excellent optical uniformity, FZ silicon is widely used in infrared optical systems and high-power laser systems. Additionally, its superior mechanical and thermal properties make it suitable for the production of high-precision and stable optical components.
Key Features:
- High Transmission & Low Optical Absorption Coefficient:FZ silicon offers exceptional transparency in the near-infrared and visible light bands, making it ideal for manufacturing optical components with high transmittance.
- High Purity & Low Impurity Content:During the zone melting process, there is no crucible contamination or seed crystal contamination, ensuring the high purity of the material with a very low optical absorption coefficient.
- Excellent Optical Uniformity:The crystal structure is uniform with a low defect density, which enhances the stability and reliability of optical components and reduces optical losses.
- Superior Mechanical & Thermal Properties:FZ silicon possesses high Young's modulus, shear modulus, and hardness, allowing it to withstand significant mechanical stress and thermal variations in optical systems.
- Good Thermal Stability:It has a high Debye temperature and Poisson's ratio, which makes it well-suited for high-temperature applications, ensuring stable performance in optical systems.
Applications:
- Infrared Optical Systems:FZ silicon is widely used in the manufacturing of infrared optical lenses, windows, and domes, especially for high-precision infrared optical systems.
- High-Power Laser Systems:FZ silicon is commonly used to produce optical windows, mirrors, and domes for high-power laser systems, where it provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock.
- High-Precision Optical Devices:Suitable for manufacturing optical components that require high uniformity and low defect density, such as laser systems, lenses, and prisms.
- High-Stability Applications:Thanks to its high mechanical strength and excellent thermal properties, FZ silicon is also used to produce optical instruments and devices that must maintain stable performance in extreme environments.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 1.2-15 μm |
| Refractive Index | 3.41776 @ 10μm |
| Reflection Loss | 46.1% @ 10μm |
| Structure | Single crystal, synthetic |
| Cleavage Planes | <111 |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 2.33 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1414 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 163 W/(m·K) @ 313K |
| Thermal Expansion | 2.6 × 10⁻⁶/K @ 293K |
| Knoop Hardness | 1100 kg/mm² |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 712.8 J/(kg·K) |
| Dielectric Constant | 13 @ f = 9.37 GHz |
| Young's Modulus | 130.91 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 79.92 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | 101.97 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.266 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| Molecular Weight | 28.09 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
| Material Name | FZ Silicon Crystals |
| Available Size | 3-200mm |
| Growing Method | FZ |
| Transmittance Range | 1-14μm |
| Crystal Structure | Monocrystalline |
| Orientation | <100>, <111>, <110> |
| Blank Shape | Round, rectangular, wedge, lens, step drilled, special-shaped |
| Report | Compliance with ROHS and REACH reports |
| Report | Compliance with ROHS and REACH reports |
 new material
new material