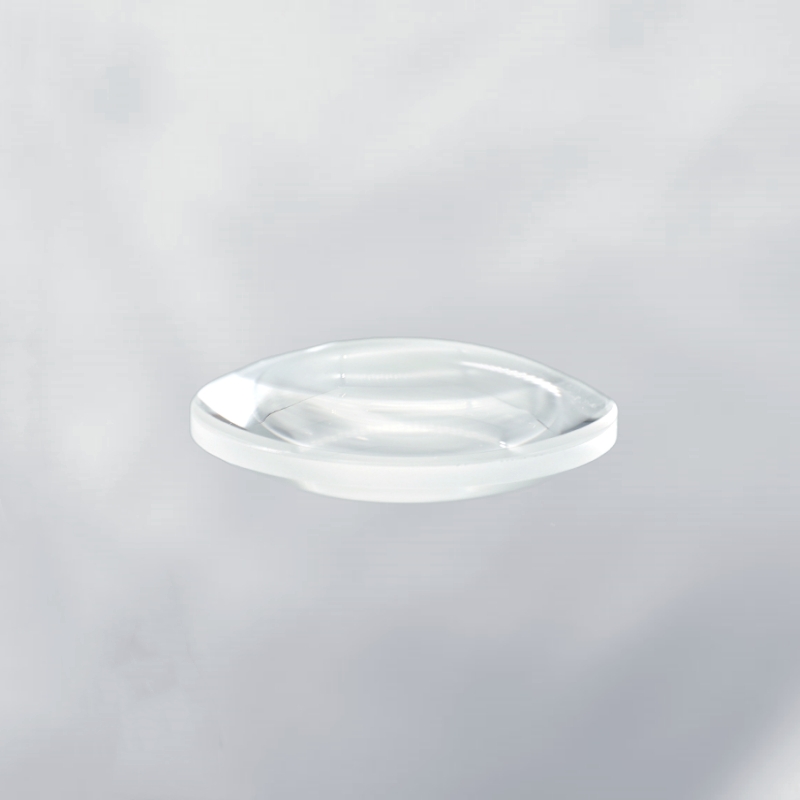
Barium fluoride double-convex lens is a high-performance optical component designed for efficient light convergence, minimized spherical aberration, and superior ultraviolet and infrared transmission. Manufactured from high-purity BaF₂, it offers exceptional optical clarity, strong resistance to environmental degradation, and excellent thermal stability. This precision lens is widely used in laser systems, spectroscopy, aerospace applications, and scientific instrumentation, ensuring optimal light manipulation and performance for advanced optical systems.
Product Overview
The barium fluoride double-convex lens is an optical element made from barium fluoride material, designed with two convex surfaces. It is primarily used to converge light from a point source or transmit light to other optical systems. With its excellent optical properties, the barium fluoride double-convex lens provides high light transmission and superior performance across the UV, visible, and infrared spectra. It allows for better light control and clearer images. Its robust structure ensures stable performance even in extreme conditions such as high temperature and pressure.
Key Features
- High Transmission: Excellent light transmission across UV, visible, and infrared wavelengths.
- High Stability: High hardness and wear resistance, ensuring stable operation in extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Low Reflection and Scattering: Minimizes light loss and dispersion, ensuring efficient light transmission.
- High Refractive Index and Dispersion: Suitable for use in dispersion systems such as prisms to effectively separate light of different wavelengths.
Applications
- Telescopes and Microscopes: Used for image focusing and imaging, providing clear views.
- Laser Systems: Used for focusing laser beams, improving beam transmission efficiency and stability.
- Optical Instruments: Applied in cameras, LiDAR systems, and other optical devices for precise optical control.
- Infrared Spectroscopy and Imaging: Excellent transmission performance in the infrared spectrum, widely used in infrared spectroscopy and imaging equipment.
- Fiber Optic Communication and Sighting Systems: Used for beam focusing and collimation, enhancing optical system performance.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 0.15-14 μm |
| Transmittance | >94%@0.35nm-10.8μm |
| Refractive Index | 1.462@2.58μm, 1.45@5μm |
| Reflection Loss | 6.8%@2.58μm (both surfaces) |
| 6.5%@5μm (both surfaces) | |
| 5.3%@10.35μm (both surfaces) | |
| Absorption Coefficient | 3.2×10⁻⁴@6μm |
| Structure | Cubic Crystal System |
| Cleavage Planes | <111 |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 4.89 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1386 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 11.72 W/(m·K) @ 286K |
| Thermal Expansion | 18.1×10⁻⁶/K @ 273K |
| Knoop Hardness | 82 kg/mm² |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 410 J/(kg·K) |
| Dielectric Constant | 7.33 @ 1 MHz |
| Young's Modulus | 53.07 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 25.4 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | 56.4 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.343 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | 1.7 g/L @ 20℃ |
| Molecular Weight | 175.3238 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
| Diameter Range | 2-300mm |
| Focal Length | 15-5000mm |
| Thickness | 0.12-60mm |
| Surface Quality | 80-50, 60-40, 40-20, 20-10, 10-5 |
| Surface Flatness | λ/2, λ/4, λ/8, λ/10 |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Coating | Customizable |
 new material
new material