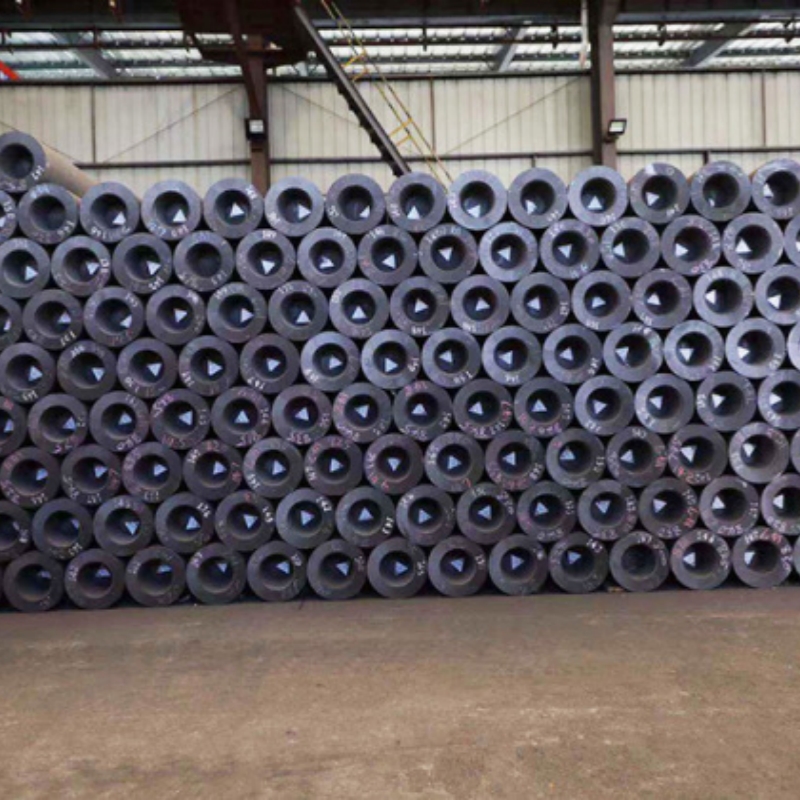
The 250 impregnated graphite electrode is a high-performance carbon-based electrode designed for industrial applications requiring superior electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, and mechanical strength. Manufactured using precision impregnation techniques, this graphite electrode exhibits optimized density, enhanced oxidation resistance, and extended lifespan. It is widely used in electric arc furnaces, metal refining, chemical processing, and electrochemical applications, ensuring reliable and efficient energy transfer in demanding environments.
Product Overview
The 250 Impregnated Graphite Electrode is made from high-quality graphite powder and undergoes an impregnation treatment to further enhance its electrical conductivity and high-temperature performance. This electrode is widely used in high-temperature electric arc furnaces, metallurgy, electrolysis equipment, and other industrial applications. The unique impregnation process improves the electrode’s strength, conductivity, and heat resistance, allowing it to perform well under complex working conditions.
Key Features
- Excellent Electrical Conductivity: Ensures high-efficiency current conduction during the smelting process.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Suitable for high-temperature operations, capable of withstanding the intense heat of the electric arc and high electrical loads.
- High Mechanical Strength: Enhanced compressive strength ensures that the electrode will not experience premature wear or damage during use.
- Impregnation Process: The advanced impregnation technique improves the durability and stability of the graphite electrode.
- Thermal Shock Resistance: Maintains stability under environments with rapid temperature changes, reducing the risk of damage due to thermal shock.
Applications
- Metallurgy Industry: Used in steel smelting and electric arc furnaces as high-temperature electrodes.
- Aluminum Smelting: Applied in the electrolysis of aluminum, particularly in aluminum electrolysis cells.
- Electrolysis Equipment: Widely used in various electrolysis devices, providing stable current transmission.
- Industrial Heating Equipment: Used in industrial heating furnaces to provide efficient current conduction.
- New Energy Sector: Can be utilized in the production of new energy batteries and high-power electrolysis processes.
| Item | Unit | Nominal Diameter (mm) | ||||||
| 75-200 | 250-400 | 450-600 | ||||||
| Premium Grade | First Grade | Premium Grade | First Grade | Premium Grade | First Grade | |||
| Resistivity ≤ | Electrode | μΩm | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| Joint | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | |||||
| Flexural Strength ≥ | Electrode | MPa | 10 | 9 | 8 | |||
| Joint | 13 | 13 | 13 | |||||
| Elastic Modulus ≤ | Electrode | GPa | 12 | 12 | 12 | |||
| Joint | 14 | 14 | 14 | |||||
| Density ≥ | Electrode | g/cm³ | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.65 | |||
| Joint | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.72 | |||||
| Thermal Expansion ≤ | Electrode | 10⁻⁶/℃ | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | |||
| Joint | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |||||
| Ash Content ≤ | % | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||||
 new material
new material