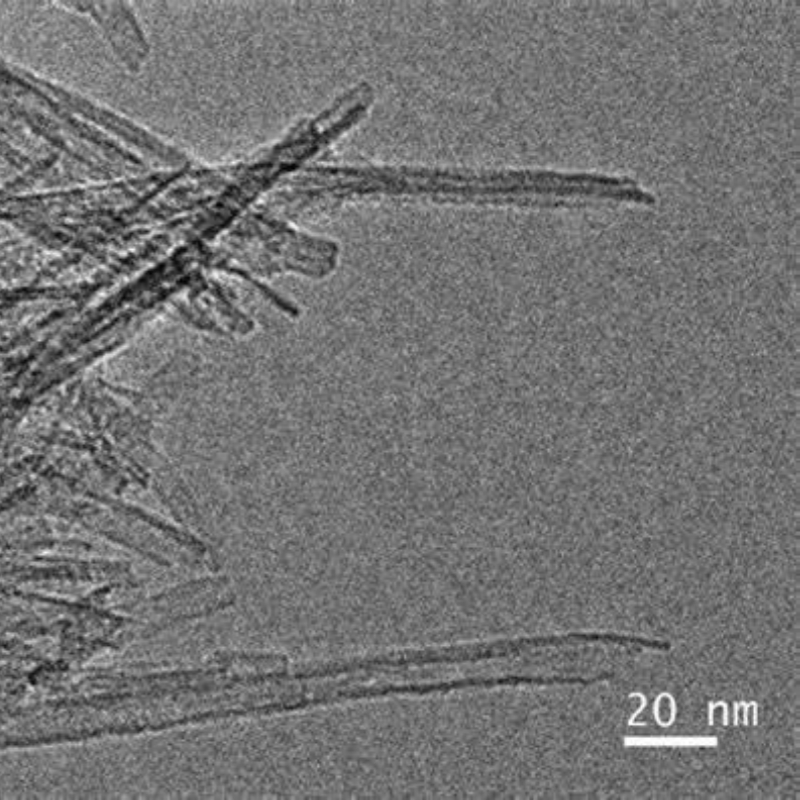
Titanium Oxide-B nanotubes provide optimized charge transport efficiency, superior structural stability, and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Designed for catalysis, energy storage, and environmental applications, they ensure reliable performance, extended durability, and high adaptability.
Product Overview
Titanium Oxide-B (TiO₂-B) nanotubes are a nanomaterial with a unique crystal structure, belonging to the monoclinic crystal system. They feature an open structure and excellent ion transport properties. Compared to the more common anatase and rutile phases, TiO₂-B exhibits higher theoretical capacity and more efficient photocatalytic activity, making it suitable for applications in batteries and photocatalysis. This material is typically synthesized through hydrothermal reactions combined with calcination, which results in a large specific surface area, enhancing light absorption and catalytic efficiency.
Key Features
- Efficient Photocatalytic Activity:TiO₂-B demonstrates superior photocatalytic activity under light, making it ideal for applications in environmental remediation and energy conversion.
- Wide Light Absorption Range:TiO₂-B has a narrower band gap, enabling it to absorb a broader range of light wavelengths, which improves photocatalytic efficiency.
- Good Stability:This material offers excellent chemical and thermal stability, maintaining its structure and performance in various environments.
Applications
- Lithium-Ion Batteries:As an anode material for lithium-ion batteries, TiO₂-B can significantly improve the battery's specific capacity and cycling stability, offering better ion binding and transport capabilities.
- Photocatalysis:TiO₂-B has great potential in photocatalytic applications, enhancing charge separation and transport efficiency in photocatalysts. It is particularly effective in water treatment and the degradation of organic pollutants.
- Other Applications:The material also shows promise in supercapacitors, sensors, and other fields.
| Parameter | Value |
| Diameter | 8-10 nm |
| Purity | 99% |
| Length | 100-200 nm |
| Surface Area | 200-300 m²/g |
 new material
new material