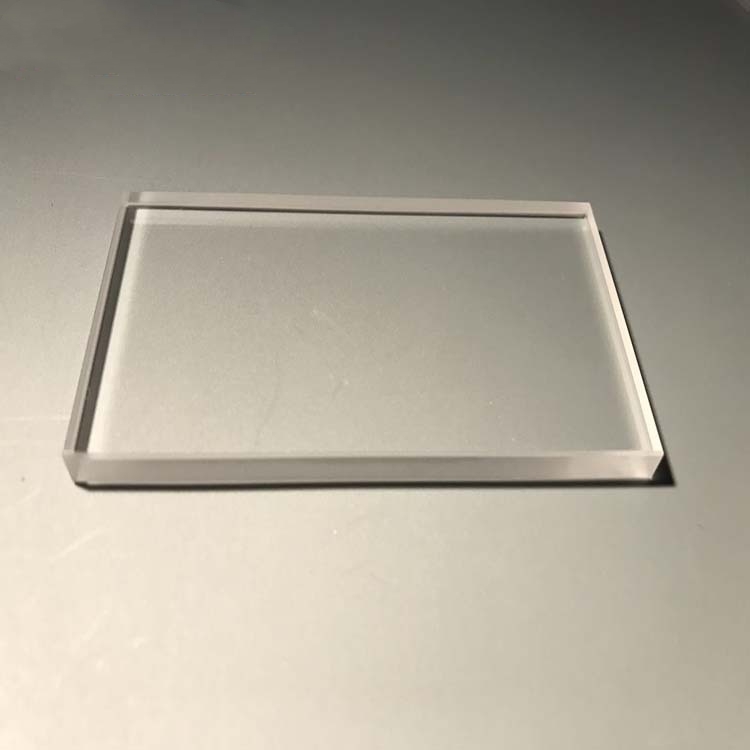
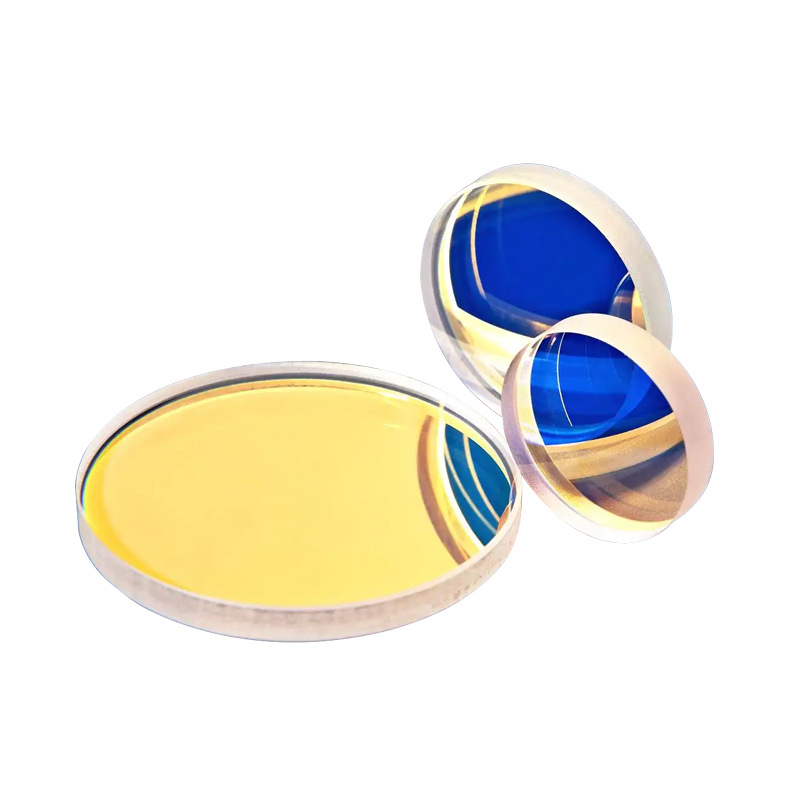
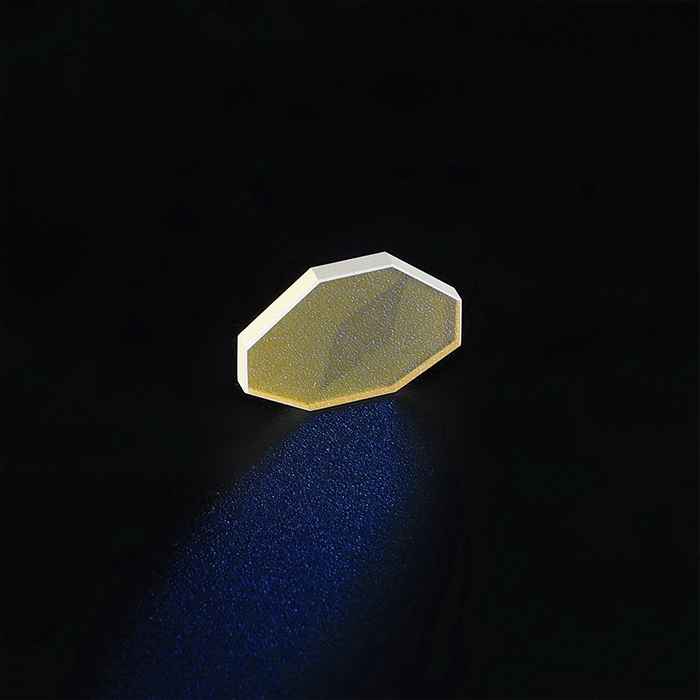
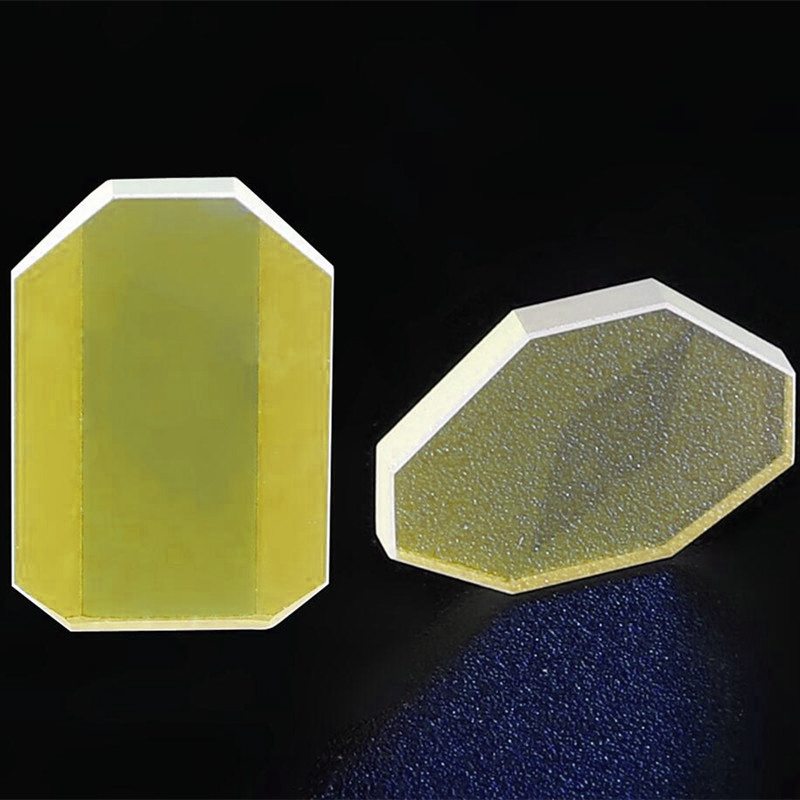
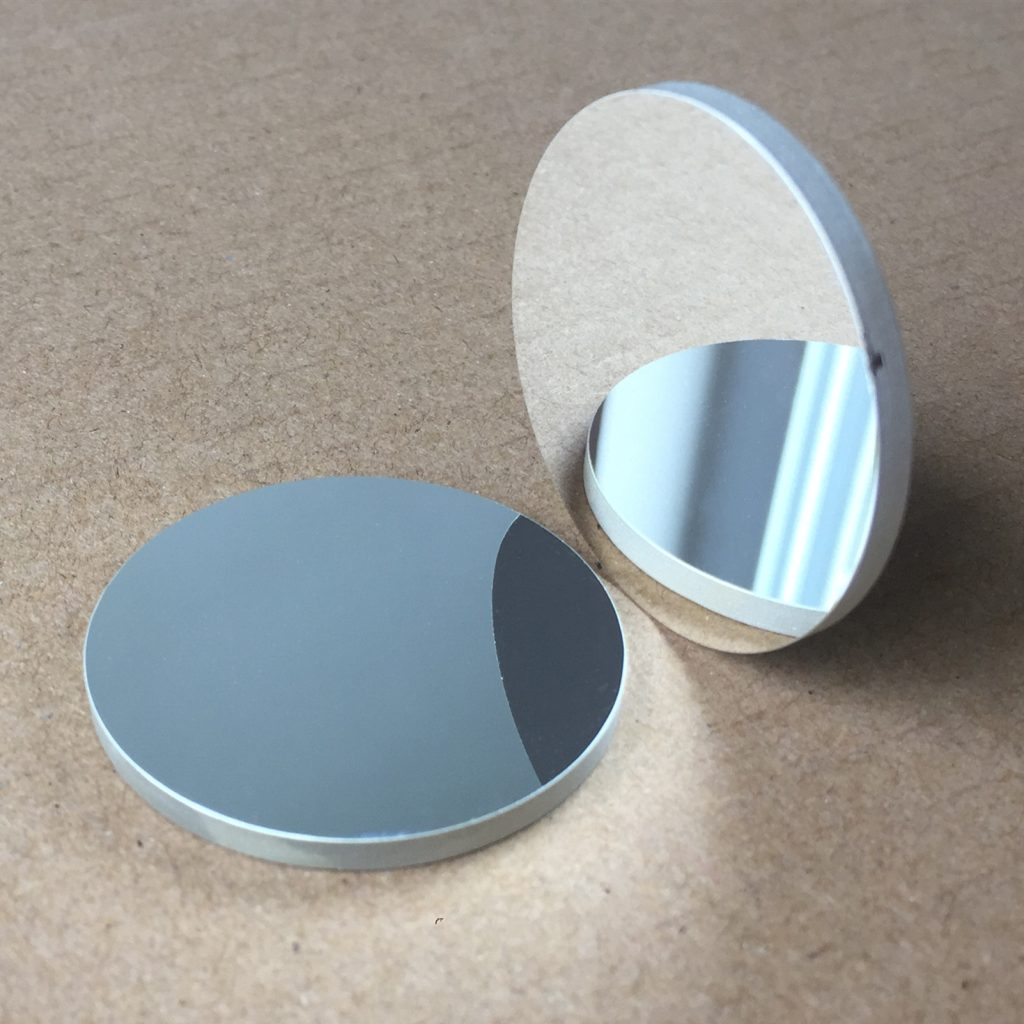
Quartz vibrating mirror is a precision optical component designed for dynamic beam steering, rapid optical modulation, and controlled light reflection. Manufactured from high-purity quartz, it offers excellent thermal stability, high reflectivity across various wavelengths, and strong resistance to environmental variations. This mirror is widely used in laser scanning systems, adaptive optics, lidar technology, and scientific instrumentation, ensuring reliable performance in high-speed optical applications.
Product Overview
The Quartz Vibrating Mirror is an optical component made from high-quality quartz glass, commonly used in laser marking, laser cutting, and laser welding applications. Quartz is known for its excellent light transmission, high-temperature resistance, and chemical stability, allowing the mirror to maintain stable performance in harsh environments. Its primary function is to control the scanning direction and speed of laser beams, enabling precise laser path adjustments and focal positioning for pattern generation and surface treatment.
Key Features
- High Light Transmission: Quartz material can transmit a wide range of light spectra from ultraviolet to far infrared, reducing light energy loss and improving the efficiency of laser systems.
- High Heat Resistance: The quartz vibrating mirror can withstand high-temperature working environments while maintaining optical performance stability.
- High Chemical Stability: Resistant to corrosion from various chemical environments, making it suitable for harsh working conditions.
- High Precision and Stability: Capable of precise laser beam scanning and positioning, ensuring high-quality marking and cutting results.
- Long Service Life: Offers a long lifespan, resistant to both high and low-temperature environments, meeting the demands of various industrial applications.
Applications
- Laser Marking: Used for precise marking of object surfaces, widely applied in industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
- Laser Cutting: In laser cutting machines, it controls the precise scanning of laser beams, suitable for cutting metals, plastics, glass, and other materials.
- Laser Welding: In laser welding equipment, it precisely controls the scanning and focal position of the laser beam to ensure high-quality welds.
- Laser Engraving: Achieves high-precision engraving for applications in artwork, electronics, and other industries.
- Precision Laser Processing: Widely used in precision processing technologies such as micro-machining and surface treatment.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 0.18-2.1 μm |
| Refractive Index | 1.4585 @ 0.5876 μm |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 2.21 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1900 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.35 W/(m·℃) |
| Thermal Expansion | 4.0 × 10⁻⁶ /℃ |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.728 × 10⁻³ J/(kg·℃) |
| Young's Modulus | 7.36 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 3.14 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.17 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| Property | Value |
| Beam Range | 3mm,5mm,7mm,8mm,8.5mm,10mm,12mm,14mm,15mm,16mm,18mm,20mm,30mm,35mm,50mm,70mm,80mm |
| Wavelength | 10.6μm,1064nm,1550nm,532nm,355nm,266nm |
| Surface Quality | 40-20, 20-10, 10-5 |
| Surface Flatness | 位/4, 位/8, 位/10 |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Coating | Metal Reflective Film, Dielectric Film |
 new material
new material