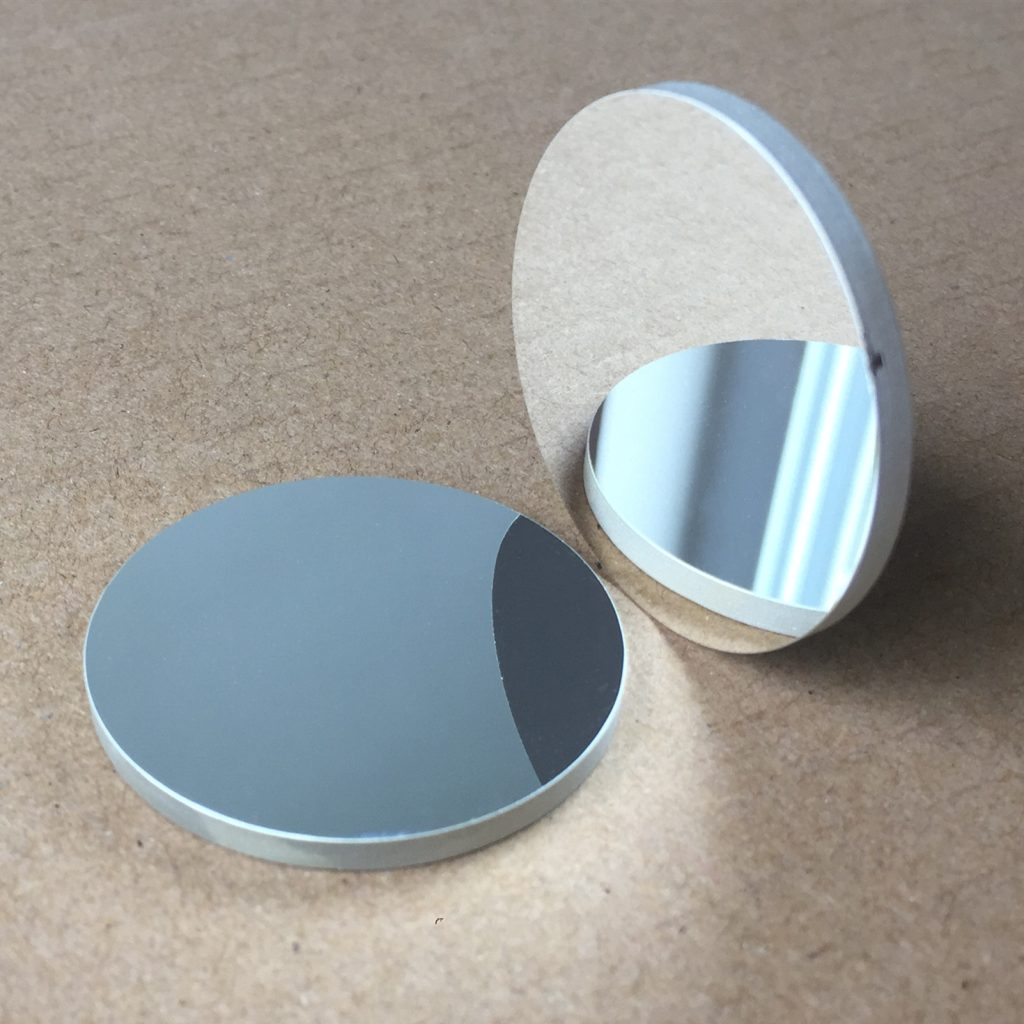
Hydrated synthetic quartz material is a high-purity optical-grade quartz designed for superior thermal resistance, enhanced chemical stability, and controlled hydroxyl content. Manufactured through advanced synthesis processes, it offers excellent transparency, minimal absorption in UV and IR spectra, and improved durability. This specialized material is widely used in semiconductor fabrication, laser optics, aerospace instrumentation, and precision scientific applications, ensuring consistent performance in demanding environments requiring optical purity and moisture resistance.
Product Overview
Hydrated synthetic quartz material is made from high-purity SiCl4 using a hydrogen-oxygen flame fusion process, ensuring the product is bubble-free with excellent optical performance. The material has high transparency and stable physical properties, making it widely used in high-end optical fields. It is especially suitable for high-precision optical components and devices, meeting demanding quality standards.
Key Features
- Bubble-Free: Produced using advanced hydrogen-oxygen flame fusion technology to ensure the quartz material is free of bubbles, maintaining its excellent optical performance.
- High Transparency: Offers exceptional transparency, ideal for optical applications requiring light transmission and imaging systems.
- Excellent Optical Performance: Provides superior optical performance, suitable for precision optical systems that ensure accurate light control and transmission.
- Stable Physical Properties: Demonstrates good thermal stability and mechanical strength, even under high temperatures and other extreme conditions.
Applications
- High-End Optics: Used in the manufacture of high-precision optical components such as lenses, windows, and mirrors, offering stable optical performance.
- Optical Instruments: Widely used in high-end optical instruments to ensure precise imaging and light beam control.
- Optical Equipment: Used as a key material in various high-performance optical devices, ensuring stable operation and accuracy.
- Laser Applications: Serves as a core optical element in laser systems, providing efficient light transmission and focus control.
| Property | Value |
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.2 |
| Young's Modulus (GPa) | 71 |
| Shear Modulus (GPa) | 31 |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.15 |
| Bending Strength (MPa) | 89 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 0.92 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 49 |
| Torsional Strength (MPa) | 29 |
| Mohs Hardness | 5~6 |
| Dielectric Constant | 4 |
| Dielectric Loss Angle φ (°) (21℃/1MHZ) | 89.93 |
| tanδ (δ = 90° - φ) (21℃/1MHZ) | 1.2×10⁻³ |
| Resistivity (Ω·cm) (20℃) | >1×10³ |
| Strain Point (℃) | 920 |
| Annealing Point (℃) | 1060 |
| Softening Point (℃) | 1585 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) (20℃) | 1.33 |
| Specific Heat (J/kg·K) | 790 |
| Thermal Diffusivity (x10⁻⁷/K) | 8.17 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (x10⁻⁷/K) α: 25℃~100℃ | 5.7 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (x10⁻⁷/K) α: 25℃~200℃ | 6.4 |
 new material
new material