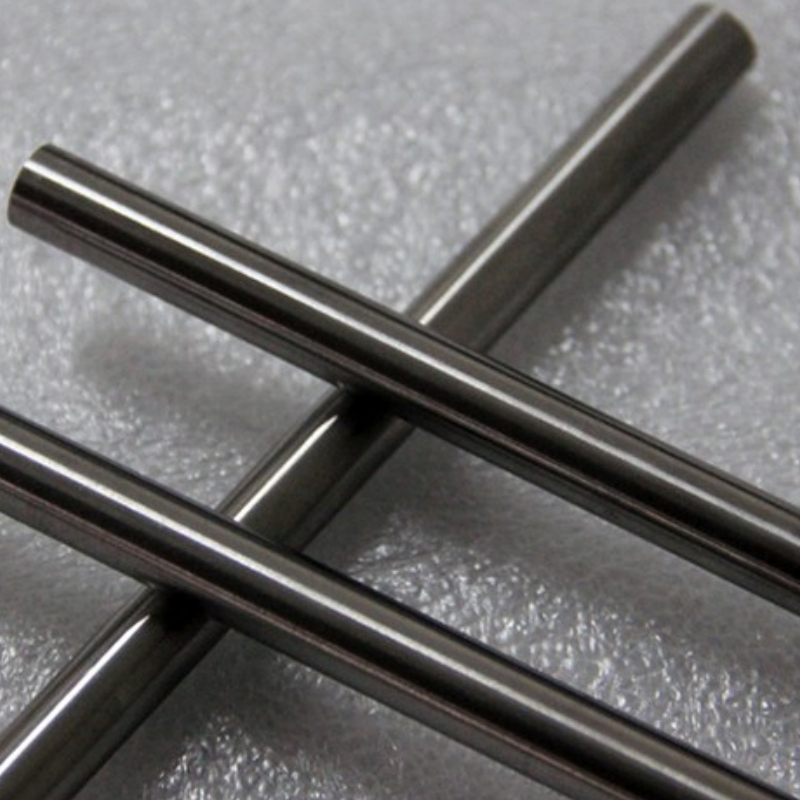
Product Overview
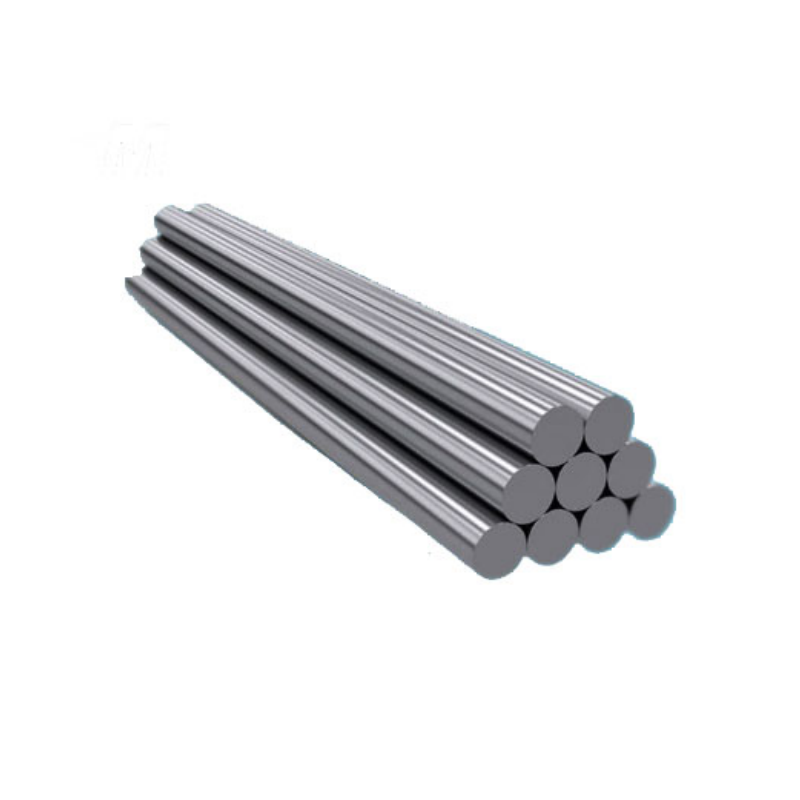
Hafnium rod is a high-purity silver-gray transition metal with excellent high-temperature and corrosion resistance properties. With a density of 13.31 g/cm³, hafnium remains chemically stable at room temperature and forms a protective oxide layer in air. In powder form, hafnium is highly reactive and can self-ignite. The rod maintains its heat resistance and oxidation resistance at high temperatures, making it ideal for applications requiring exceptional heat and corrosion resistance.
Features
- High Density and Exceptional Heat Resistance:Perfect for high-temperature environments.
- Strong Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance:Suitable for harsh and corrosive conditions.
- Stable at High Temperatures:Easy to process and customize for various applications.
- Good Thermal Conductivity:Ideal for applications that require rapid heat absorption and dissipation.
Applications
- Nuclear Industry:Due to its large neutron absorption cross-section, hafnium is used in nuclear reactors as control rods and shielding devices.
- High-Temperature Materials:Widely used in aerospace applications, hafnium rods serve as high-temperature materials for rocket nozzles, injectors, and other critical components.
- Alloy Manufacturing:Hafnium is alloyed with other metals such as tungsten and molybdenum to improve strength and heat resistance, commonly used in high-performance alloy production.
- Electronic Materials:Hafnium rods are used in high-temperature electronic devices, such as high-temperature electrodes and electron tubes.
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials:Its excellent corrosion resistance makes hafnium ideal for use in high-temperature chemical environments, including applications in the petroleum and chemical industries.
- Heat Exchange and Radiation Control:Hafnium rods are used in heat exchangers and radiation shielding, where quick heat absorption and release are essential.
| Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit | Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit | Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit |
| Li | <0.005 | ppm | Zn | <0.01 | ppm | Pb | <0.01 | ppm | |||
| B | <0.001 | ppm | Ga | <0.01 | ppm | Bi | <0.01 | ppm | |||
| F | <0.05 | ppm | Ge | <0.01 | ppm | Y | <0.05 | ppm | |||
| Na | 0.11 | ppm | As | <0.005 | ppm | Th | <0.001 | ppm | |||
| Mg | 0.01 | ppm | Se | <0.05 | ppm | Er | <0.005 | ppm | |||
| Al | 0.08 | ppm | Zr | 0.29 | wt% | Ru | <0.005 | ppm | |||
| Si | 0.23 | ppm | Nb | 0.54 | ppm | Rh | <0.01 | ppm | |||
| P | 0.006 | ppm | Mo | 0.39 | ppm | Os | <0.05 | ppm | |||
| Cl | <0.05 | ppm | Pd | <0.05 | ppm | Cd | <0.05 | ppm | |||
| K | 0.02 | ppm | Ag | <0.05 | ppm | In | 0.01 | ppm | |||
| Ca | 0.02 | ppm | Sn | <0.05 | ppm | ||||||
| Ti | 0.07 | ppm | Sb | <0.05 | ppm | ||||||
| V | <0.005 | ppm | Ba | <0.05 | ppm | ||||||
| Cr | 0.06 | ppm | Hf | Matrix | wt% | ||||||
| Mn | <0.005 | ppm | Ta | <5 | ppm | C | 20 | ppm | |||
| Fe | 1.9 | ppm | W | 0.03 | ppm | S | 0.07 | ppm | |||
| Co | <0.005 | ppm | Pt | <0.1 | ppm | O | 40 | ppm | |||
| Ni | 0.06 | ppm | Au | <0.05 | ppm | N | <10 | ppm | |||
| Cu | <0.05 | ppm | Hg | <0.05 | ppm | H | 6 | ppm |
 new material
new material