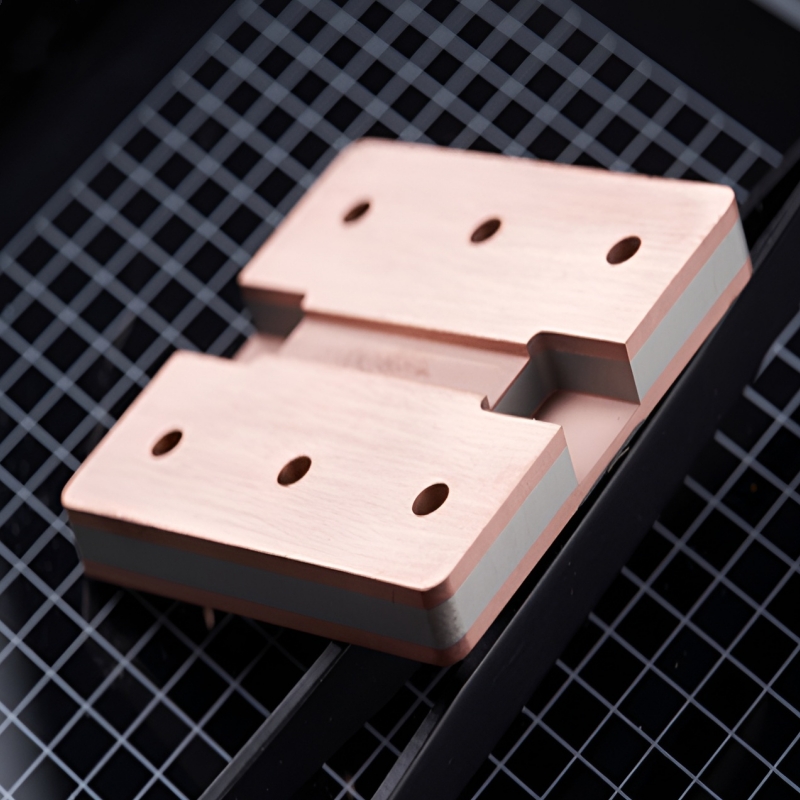
Product Overview
CPC (Copper Molybdenum Copper) is a composite material consisting of copper and molybdenum, with a copper-clad molybdenum core structure. The typical structure ratio is Cu:Mo-Cu:Cu 1:4:1. This material combines the excellent electrical conductivity of copper with the high-temperature stability of molybdenum, offering higher thermal conductivity and lower cost compared to traditional materials like W(Mo)-Cu and Cu/Mo/Cu. CPC is widely used in electronic packaging applications that require high thermal conductivity and thermal stability, particularly in RF, microwave, and high-power semiconductor devices.
Key Features
- High Thermal Conductivity:Provides superior heat dissipation compared to traditional W(Mo)-Cu and Cu/Mo/Cu materials.
- Excellent Interface Bonding:Can withstand thermal shock up to 850°C, ensuring reliability under high thermal stress.
- Ease of Machining:Easier to process and stamp into large components compared to CMC (Copper Matrix Composites).
- Non-Magnetic:Suitable for applications with strict magnetic requirements.
- Cost Advantage:More affordable compared to other high-thermal-conductivity materials, offering a cost-effective solution without compromising performance.
Applications
- RF and Microwave Devices:Ideal for RF, microwave components, and high-power semiconductor packaging.
- Semiconductor Industry:Used for packaging high-power semiconductor devices, ensuring effective heat dissipation and thermal management.
- Electronics Packaging:Widely used in electronic packaging applications where high thermal conductivity and high-temperature resistance are required.
- High-Power Devices:Provides excellent thermal management for high-power devices, ensuring stable heat conduction and temperature control.
| Cu/Mo70Cu/Cu Thickness Ratio | Density (g/cm²) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10^-9 / K) 10-9/k | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) W/m.K | ||
| 1:4:1 | 9.46 | X-y | X-Z | X-y | X-Z |
| 7.2 | 9 | 340 | 300 | ||
 new material
new material