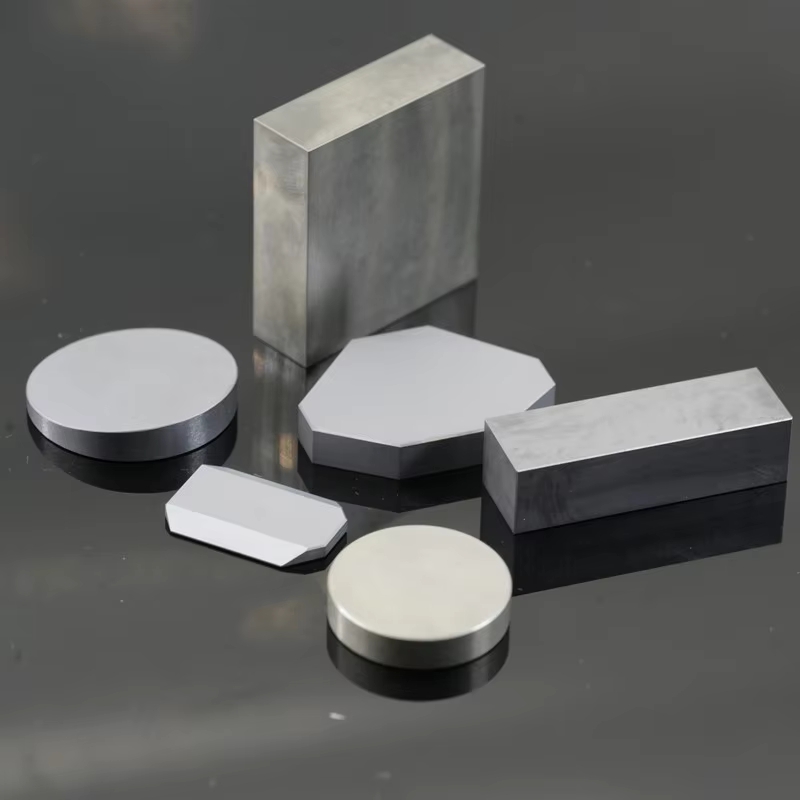
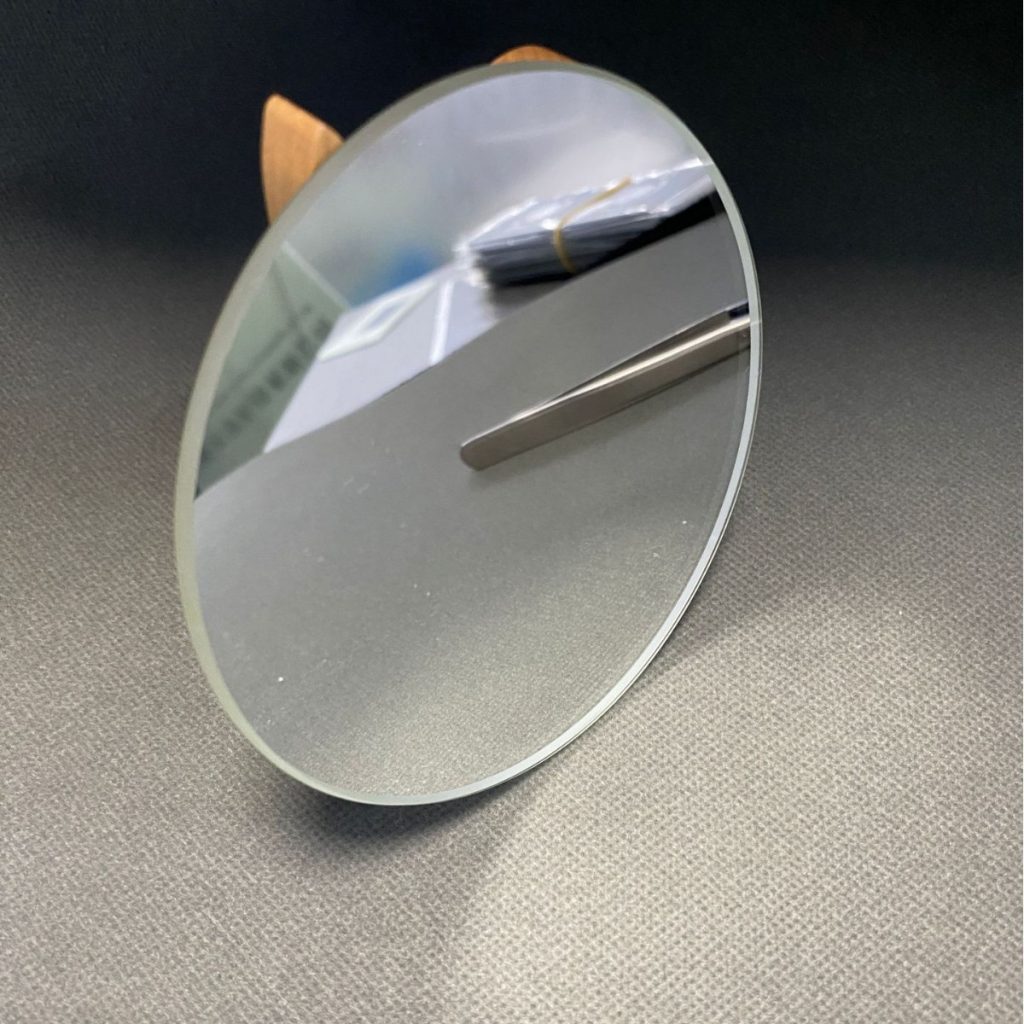
Single-crystal germanium (Ge) is a high-purity semiconductor and infrared optical material known for its superior transmission in the mid-infrared range, excellent electrical properties, and strong resistance to thermal and mechanical stress. Manufactured through precise crystal growth techniques, it provides exceptional optical clarity, controlled charge carrier mobility, and optimized wavelength performance. This material is widely used in infrared optics, semiconductor applications, photodetectors, and high-precision scientific instrumentation, ensuring reliable performance across demanding environments.
Product Overview:
Single-crystal germanium is a material with excellent optical and electronic properties, featuring a cubic crystal structure. Its stable atomic structure and high degree of order give it outstanding performance in both optical and electrical applications. With a high carrier mobility and moderate bandgap, single-crystal germanium effectively absorbs and emits light in specific wavelengths, particularly in the infrared (IR) region. It is widely used in optoelectronics, fiber-optic communications, high-speed electronics, and infrared optical devices.
Key Features:
- High Carrier Mobility:Single-crystal germanium offers higher electron and hole mobility than silicon, making it ideal for high-speed electronic devices, resulting in faster operational speeds.
- Superior Optical Properties:It has excellent optical transparency, especially in the infrared region, making it suitable for infrared optical systems and detectors.
- High Refractive Index & Low Absorption:These characteristics make germanium an ideal material for infrared optical elements, particularly in infrared detection and imaging systems.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range:Compared to silicon, single-crystal germanium operates effectively over a wider temperature range, making it suitable for extreme environmental conditions.
- High Stability:Germanium exhibits high sensitivity, fast response, and long-term stability, ensuring its reliability in high-performance devices.
Applications:
- Optoelectronics:Used in manufacturing various optoelectronic devices such as lasers, photodetectors, and fiber-optic communication systems.
- Infrared Detection & Imaging:Widely used in infrared imaging systems and night-vision devices, offering high precision and sensitivity for detection.
- Infrared Optical Devices:Ideal for producing infrared lenses, windows, mirrors, and other high-performance optical components.
- High-Speed Electronic Devices:Due to its high electron mobility, single-crystal germanium is suited for high-speed electronic components and semiconductor applications.
- Solar Cells & Thermoelectric Devices:Used in the manufacturing of efficient solar cells and thermoelectric devices for energy conversion.
- Radiation Sensors:With its excellent optical and electrical properties, single-crystal germanium is also widely applied in radiation sensors.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 2-15 μm |
| Reflection Loss | 4.0028 @ 10.6 μm |
| Absorption Coefficient | 1.3 × 10⁻³ @ 3.8 μm |
| 3 × 10⁻² @ 10.6 μm | |
| Structure | Cubic Crystal System |
| Cleavage Planes | <111 |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 5.33 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 936 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 58.61 W/(m·K) @ 293K |
| Thermal Expansion | 6.1 × 10⁻⁶/K @ 298K |
| Knoop Hardness | 780 kg/mm² |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 310 J/(kg·K) |
| Dielectric Constant | 16.6 @ 9.37 GHz |
| Young's Modulus | 102.7 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 67 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | 77.2 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.28 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| Molecular Weight | 72.61 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
| Material Name | Single Crystals Germanium |
| Available Size | 3-300mm |
| Growing Method | CZ (Czochralski Method) |
| Type | N-type, P-type |
| Transmittance Range | 2-15μm |
| Crystal Structure | Monocrystalline |
| Orientation | <100>, <111> |
| Blank Shape | Round, rectangular, wedge, lens, step drilled, special-shaped |
 new material
new material