Product Overview
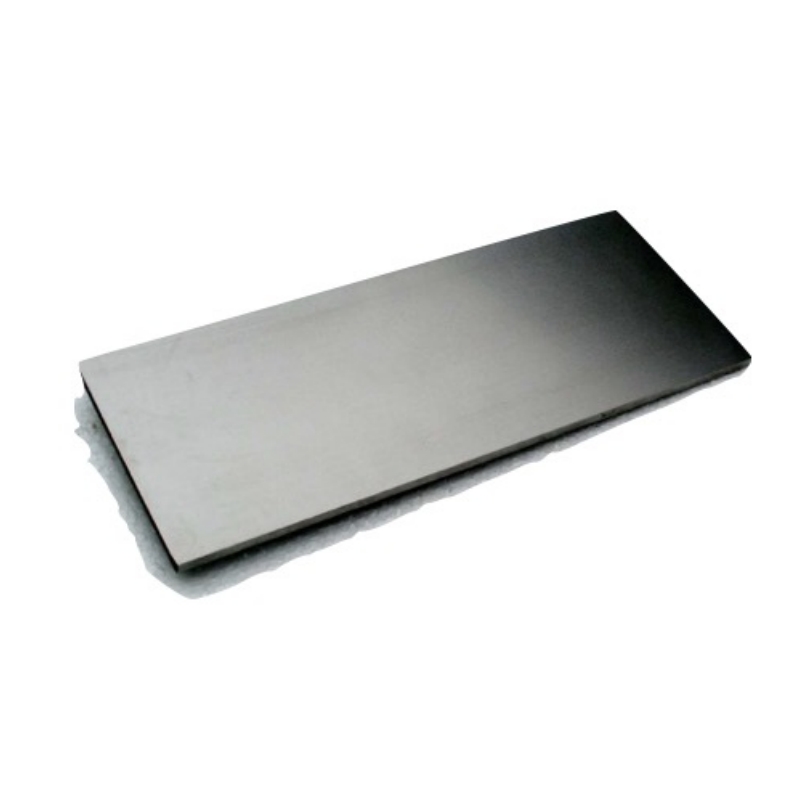
The tungsten plate is a metal sheet material made from high-purity tungsten, known for its outstanding high-temperature performance and mechanical properties. Its high density, high melting point, and excellent chemical stability make it widely applicable across industries, serving as an ideal high-temperature structural and functional material.
Key Features
- High Melting Point: The tungsten plate boasts a melting point of 3410°C, making it suitable for extreme high-temperature environments.
- High Strength: Retains excellent mechanical properties under high temperatures, providing superior resistance to thermal deformation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resilient against most acidic and alkaline media, making it ideal for chemical and corrosive environments.
- High Density: With a density of 19.35 g/cm³, the tungsten plate offers excellent mechanical strength and impact resistance.
- Chemical Stability: Tungsten does not react with air, water, or most acids and alkalis at room temperature, ensuring durability in harsh environments.
Applications
The tungsten plate finds extensive use in various industries:
- Electronics Industry: Used as substrates for high-temperature electronic components, vacuum devices, and electrode materials.
- Aerospace: Serves as high-temperature-resistant components in rocket nozzles, thermal shields, and aircraft engine parts.
- Chemical Industry: Used in corrosion-resistant reactor linings, heating elements, and chemical equipment accessories.
- Mechanical Manufacturing: Widely applied in the production of ultra-hard molds, cutting tools, and wire-drawing dies.
- Military Applications: Essential for manufacturing high-density armor-piercing rounds, artillery components, and armor materials.
- Research and Precision Manufacturing: Ideal as structural materials for high-temperature furnaces, nuclear research equipment, and critical components in ultra-high vacuum environments.
| Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit | Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit | Element | Measured Value | Standard Value | Unit |
| Li | Zn | Pb | <10 | ppm | |||||||
| B | Ga | Bi | <10 | ppm | |||||||
| F | Ge | Y | |||||||||
| Na | As | Th | |||||||||
| Mg | <30 | ppm | Se | Er | |||||||
| Al | <20 | ppm | Zr | Ru | |||||||
| Si | <50 | ppm | Nb | Rh | |||||||
| P | Mo | <100 | ppm | Os | |||||||
| Cl | Pd | Cd | |||||||||
| K | Ag | In | |||||||||
| Ca | <50 | ppm | Sn | <10 | ppm | ||||||
| Ti | Sb | <10 | ppm | ||||||||
| V | Ba | ||||||||||
| Cr | ppm | Hf | |||||||||
| Mn | Ta | C | 80 | ppm | |||||||
| Fe | <50 | ppm | W | Matrix | wt% | S | |||||
| Co | Pt | O | 50 | ppm | |||||||
| Ni | <30 | ppm | Au | N | 30 | ppm | |||||
| Cu | Hg | H |
 new material
new material