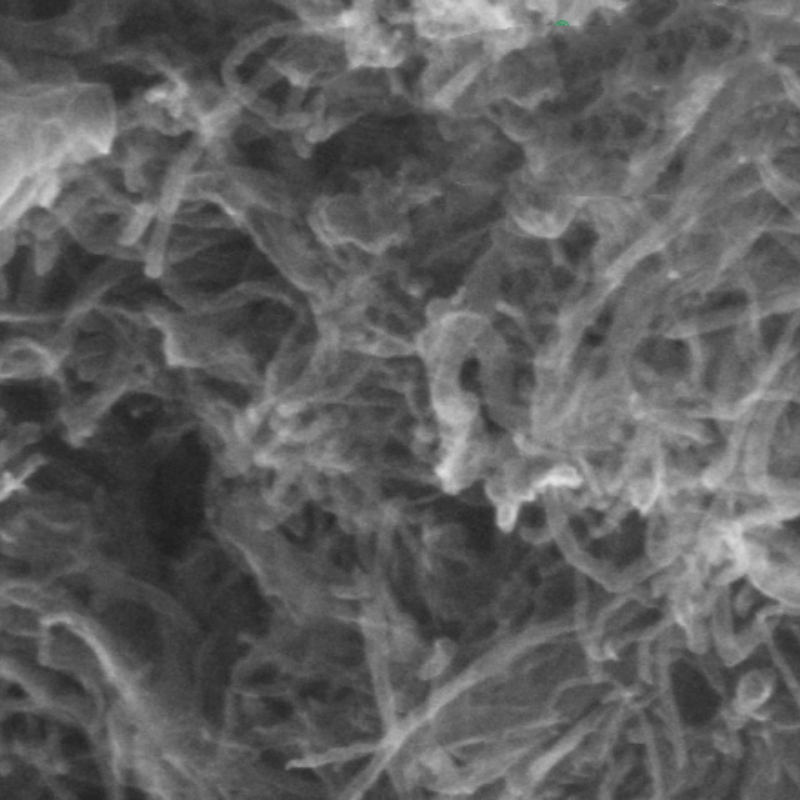
Oleic acid-modified Fe₃O₄ magnetic nanoparticles provide optimized hydrophobicity, superior colloidal stability, and enhanced magnetic responsiveness. Designed for advanced biomedical and industrial applications, they ensure efficient dispersion, extended lifespan, and high adaptability.
Product Overview
Oleic acid-modified Fe₃O₄ magnetic nanoparticles are synthesized using the coprecipitation method, where oleic acid acts as a surface modifier, imparting oil solubility to the nanoparticles. This modification allows the nanoparticles to disperse in organic solvents such as n-hexane and chloroform. By optimizing the reaction conditions, the nanoparticles exhibit superparamagnetism, high biocompatibility, and excellent dispersibility, making them ideal for applications in biomedical fields, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and environmental remediation.
Key Features
- Superparamagnetism: These nanoparticles possess superparamagnetic properties, allowing them to quickly magnetize and demagnetize in an external magnetic field, making them suitable for MRI and magnetic hyperthermia (MHT) applications.
- Oil Solubility: The oleic acid modification imparts oil solubility to the Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles, enabling them to disperse in solvents like chloroform and n-hexane, ideal for oil-phase systems.
- Surface Modification: The oleic acid modification enhances nanoparticle stability and provides surface groups that can be further modified, facilitating the conjugation of chemical or biological molecules.
- Stability: The oleic acid coating improves the physical and chemical stability of the nanoparticles, ensuring their performance remains consistent across various storage and application environments.
Applications
- MRI Contrast Agent: Due to their superparamagnetism, these oleic acid-modified Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles can serve as negative contrast agents for MRI, significantly enhancing image contrast and aiding in the clear visualization of tissues and organs.
- Biosensing and Detection: In biosensors, the Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles act as signal transducers or enhancers, improving detection sensitivity and selectivity.
- Water-in-Oil Nanoemulsions: Oleic acid-modified Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles can be dispersed in oil phases to enhance the functionality of water-in-oil nanoemulsions.
- Environmental Remediation: These nanoparticles are useful for adsorbing and separating pollutants, particularly in water treatment and soil remediation applications.
| Technical Parameter | Description |
| Form | Solid or liquid |
| Preparation Method | Co-precipitation method |
| Saturation Magnetization | ~60 emu/g Fe |
| Dispersibility | Oil-soluble, can be dispersed in solvents like n-hexane, chloroform |
| Iron Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Notes | TEM image obtained from the solution; larger particles may appear in the powder test. If morphology observation is required, it is recommended to purchase the solution. |
| Particles larger than 30nm can be separated by magnets, while particles smaller than 30nm are recommended to be separated by magnetic separation columns. | |
| The dispersibility of re-dispersed powder is worse than the dispersion liquid. For better dispersion, please choose the dispersion liquid. |
 new material
new material