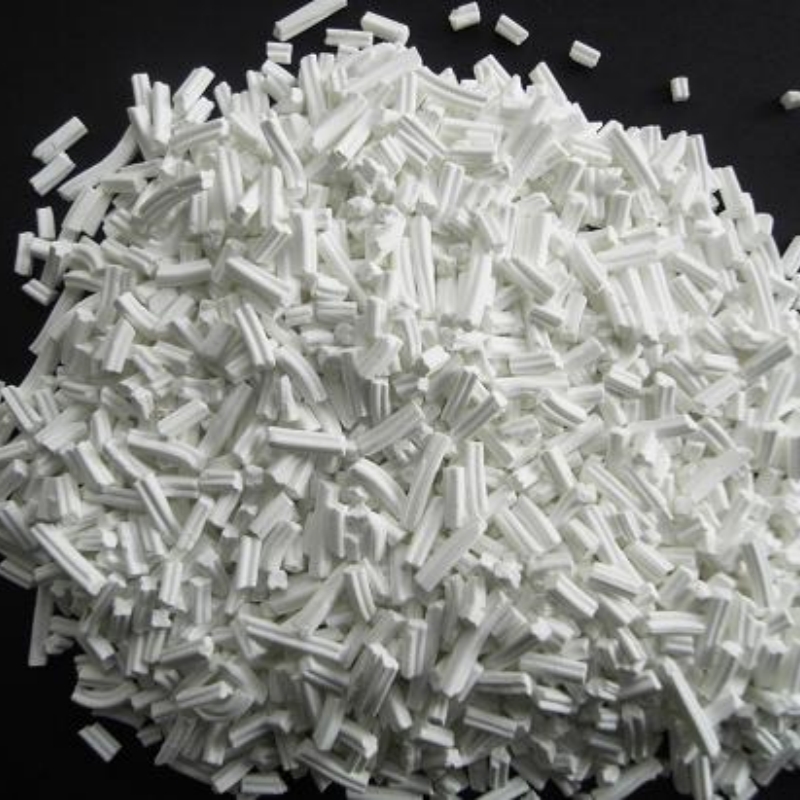
Methanol-to-Gasoline (MTG) catalyst is an advanced catalytic material designed to efficiently convert methanol into high-quality gasoline through selective hydrocarbon transformation. Engineered with optimized zeolite-based formulations, it enhances reaction kinetics, improves gasoline yield, and ensures prolonged operational stability for industrial applications. This catalyst is widely used in synthetic fuel production, alternative energy refining, and large-scale petrochemical processing, providing reliable performance for continuous gasoline synthesis operations.
Product Overview:
The Methanol-to-Gasoline (MTG) Catalyst utilizes high-efficiency molecular sieve technology to convert methanol into gasoline. The process involves dehydration to produce dimethyl ether (DME), which is further converted into light olefins, and eventually generates a mixture containing straight and branched alkanes, aromatics, and cycloalkanes. This catalyst maintains excellent selectivity and stability throughout its use, producing high-octane gasoline, with a stable increase in gasoline yield as the catalyst undergoes deactivation.
Key Features:
- High Conversion Rate & Selectivity:Achieves 100% conversion of methanol in a single pass. The gasoline produced contains less than 1% benzene, under 40% aromatics, and under 30% olefins.
- Strong Stability:The catalyst has a long single-pass lifetime, with minimal variations in gasoline yield and octane number. The catalyst can last up to 540 hours per cycle, with stable gasoline yield even after deactivation.
- High-Octane Gasoline:Gasoline produced has a research octane number (RON) of 90 or higher, ensuring high product quality.
- Low Wear Rate:Catalyst wear rate is less than 3%, extending its service life.
- Strong Adaptability:The catalyst can replace existing traditional catalysts and is suitable for various types of methanol feedstocks, including coal-based methanol, fermentation methanol, crude methanol, and refined methanol.
Applications:
- Methanol-to-Gasoline Process:Widely used in the MTG process to convert methanol, coal-based methanol, fermentation methanol, crude methanol, and refined methanol into gasoline.
- Petroleum Refining and Chemical Production:Used to replace traditional catalytic cracking techniques to produce high-octane gasoline, widely applied in refining and chemical industries.
- Gasoline Blending:Can be used to adjust gasoline components, providing high-quality blending stocks for gasoline.
| Item | Enterprise Specification | Testing Method |
| Product Type (Type) | Methanol to Gasoline Catalyst | / |
| Product ID (ID) | NKC-18 | / |
| Shape | Cylinder or Clover-like | / |
| Colour | White | Visual inspection |
| Diameter (mm) | Φ2.0×2~10 | Caliper |
| Bulk Density (g/ml) | 0.65±0.05 | Cylinder method |
| Crushing Strength (N/mm) | >10.0 | Intensity meter |
| Cation Type | H | / |
| Surface Area (BET) m²/g | ≥280 | BET |
| Adsorption (n-hexane) m/m % | / | / |
| Micro Pore Volume (Micro PV) cc/g | ≥0.27 | BET |
| Sodium Oxide (Na₂O) m/m % | ≤0.1 | Chemical method |
| Product | Yield (wt%) |
| Methanol + Ether | 0 |
| Hydrocarbons | 43.4 |
| Water | 56 |
| CO, CO₂ | 0.4 |
| Others | 0.2 |
| Total | 100 |
| Component | m% | Percentage |
| Light-end Gas | 1.4 | 0.61% |
| Propane | 5.5 | 2.39% |
| Propylene | 0.2 | 0.09% |
| Isobutane | 8.6 | 3.73% |
| n-Butane | 3.3 | 1.43% |
| Butylene | 1.1 | 0.48% |
| C5+ Gasoline Fraction | 79.9 | 34.68% |
| Total | 100 | 100% |
| Gasoline Octane | 91~95 | |
| Item | Range |
| Methanol Reactor Inlet Temperature (℃) | 260~280 |
| Methanol Reactor Outlet Temperature (℃) | 370~380 |
| Gasoline Synthesis Reactor Inlet Temperature (℃) | 350~360 |
| Gasoline Synthesis Reactor Outlet Temperature (℃) | 400~450 |
| Pressure (MPa) | 0.8~1.0 |
| Heavy Space Velocity (h⁻¹) | 1.0~2.0 |
| Item | Value |
| Dry Point | 204 |
| C5+ Gasoline | 95 |
| Actual Gums (mg/100ml) | 3 |
| C4 | 5 |
| Sulfur and Nitrogen (ppm) | ≤10 |
| Octane Value | Research Method: 93, Motor Method: 83 |
| Component | m% |
| n-Alkanes | 4.6 |
| Isoalkanes | 41.6 |
| Olefins | 9.5 |
| Naphthenes | 9.2 |
| Aromatics | 35.1 |
| Tetramethylbenzene | 1.84 |
| Distillation Point | Temperature (℃) |
| 10% | 61 |
| 50% | 99 |
| 90% | 166 |
 new material
new material