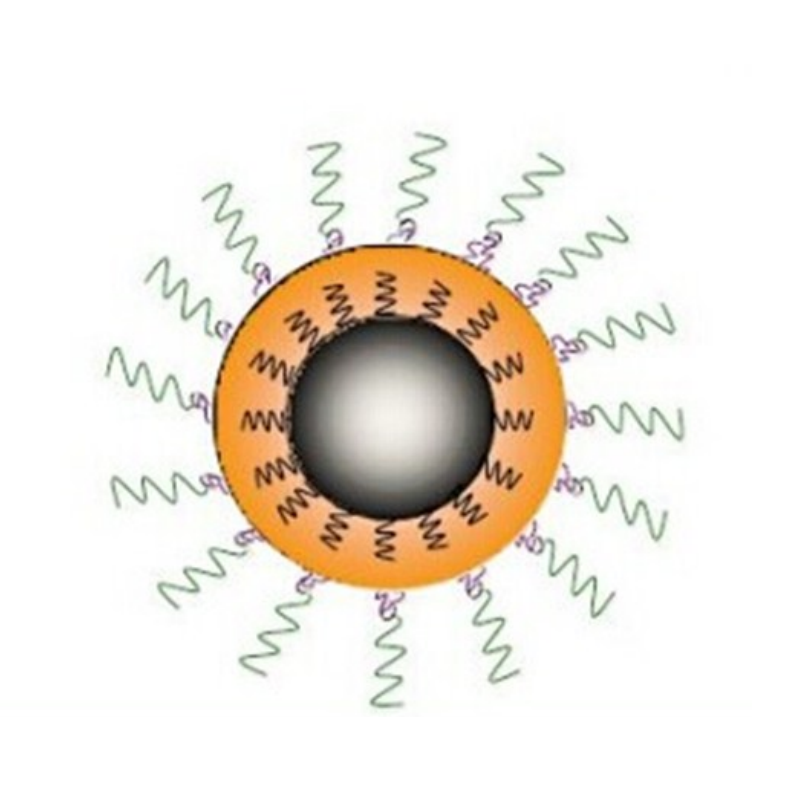
Manganese-zinc ferrite nanocrystals synthesized via the high-temperature pyrolysis method provide optimized magnetic properties, superior colloidal stability, and enhanced thermal resistance. Designed for advanced applications, they ensure efficient dispersion, extended durability, and high-performance adaptability.
Product Overview
Manganese-zinc ferrite is a composite metal oxide composed of manganese, zinc, and iron oxides, with a spinel structure and the chemical formula (Zn,Mn)Fe₂O₄. Manganese-zinc ferrite nanocrystals prepared by high-temperature pyrolysis exhibit excellent magnetic properties and crystallinity, making them suitable for various applications such as magnetic hyperthermia and bioseparation.
Features
- Magnetic Properties: Exhibits high saturation magnetization and coercivity, demonstrating excellent magnetic behavior.
- Nanometer Size Effect: Due to its nanoscale size, the material has a large specific surface area and unique physical and chemical properties.
- Good Crystallinity: Features a well-developed crystalline structure that enhances its physical and chemical performance.
Applications
- Magnetic Hyperthermia: Generates heat under the influence of an external magnetic field, used in the treatment of tumors and other diseases.
- Bioseparation: Suitable for separating specific biomolecules or cells, widely used in biomedical research.
- Magnetic-Responsive Smart Materials: Used in the development of smart materials responsive to magnetic fields, with applications in high-tech industries.
| Technical Parameter | Description |
| Main Components | Manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles prepared by high-temperature pyrolysis, chloroform |
| Saturation Magnetization | Approximately 100 emu/g Fe |
 new material
new material