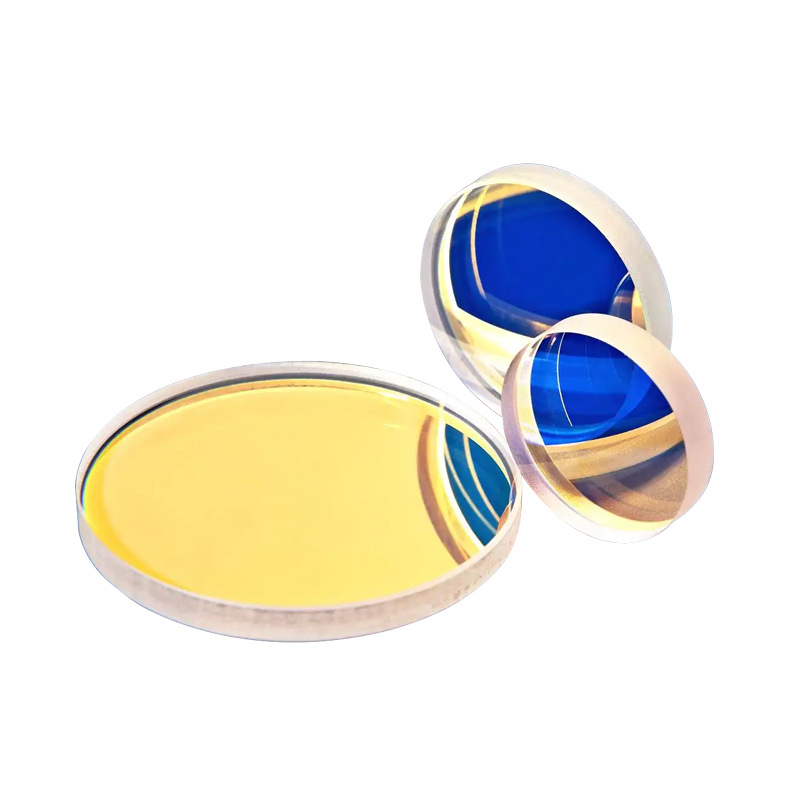
Silicon plano-convex lens is a high-performance optical component designed for superior infrared transmission, precise light focusing, and excellent durability. Manufactured from high-purity crystalline silicon, it offers outstanding optical clarity, minimal optical distortion, and strong resistance to environmental fluctuations. This precision lens is widely used in infrared imaging, laser optics, aerospace applications, and scientific research, ensuring optimal performance for advanced optical systems.
Product Overview
The silicon plano-convex lens is an optical component made from silicon, known for its high thermal conductivity and excellent optical properties. The lens features one flat surface and one convex surface, allowing it to focus light or change the size of an image. It is widely used in optical systems operating in the near-infrared and mid-infrared wavelengths. Silicon plano-convex lenses are primarily used in equipment such as LiDAR systems, optical sensors, and spectrometers, serving as components for light transmission or reflection. Additionally, they are commonly used in the solar energy sector as window materials to enhance photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Key Features
- High Thermal Conductivity: Silicon offers excellent heat dissipation, making it suitable for high thermal load applications.
- High Refractive Index and Low Dispersion: The high refractive index effectively focuses light, while low dispersion ensures high-quality imaging.
- Optical Precision: Manufactured with precision machining techniques to ensure high accuracy and excellent surface quality.
- Wide Wavelength Range: Especially suitable for optical applications in the near-infrared and mid-infrared regions.
- Versatile Optical Design: Capable of altering the direction, shape, and size of light to meet different imaging requirements.
Applications
- LiDAR: Used in LiDAR systems for beam focusing and collimation.
- Optical Sensors: Used in optical sensors to collect and process light signals.
- Spectrometers: Serves as an optical component in various spectrometer instruments.
- Solar Energy: Used as window material in solar cells to enhance photoelectric conversion efficiency.
- Medical and Military: Used in medical imaging and military applications to improve optical system performance.
- Optical Instruments: Employed in a variety of optical instruments for changing the shape, size, or direction of light beams.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 1.2-15 μm |
| Refractive Index | 3.41776 @ 10μm |
| Reflection Loss | 46.1% @ 10μm |
| Structure | Single crystal, synthetic |
| Cleavage Planes | <111 |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 2.33 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1414 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 163 W/(m·K) @ 313K |
| Thermal Expansion | 2.6 × 10⁻⁶/K @ 293K |
| Knoop Hardness | 1100 kg/mm² |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 712.8 J/(kg·K) |
| Dielectric Constant | 13 @ f = 9.37 GHz |
| Young's Modulus | 130.91 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 79.92 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | 101.97 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.266 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| Molecular Weight | 28.09 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
| Diameter Range | 2-300mm |
| Focal Length | 15-5000mm |
| Thickness | 0.12-60mm |
| Surface Quality | 80-50, 60-40, 40-20, 20-10, 10-5 |
| Surface Flatness | λ/2, λ/4, λ/8, λ/10 |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Coating | Customizable |
Submit Your RequirementsWe will contact you within 24 hours.
 WOBO Scientific Research New Materials One-Stop Service Platform
WOBO Scientific Research New Materials One-Stop Service Platform