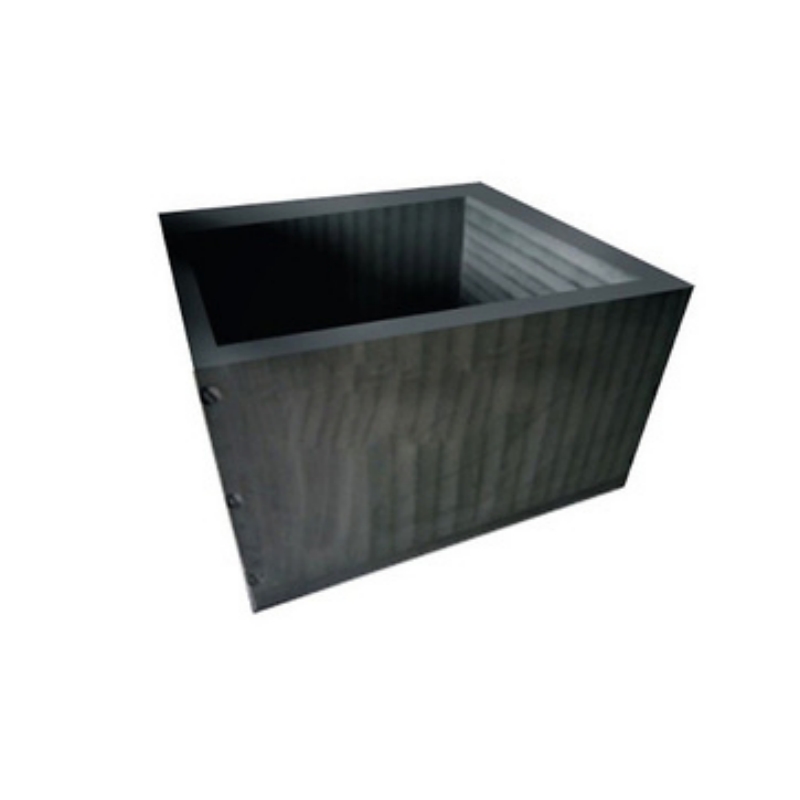
Graphite protective plates are high-purity carbon components engineered for superior thermal resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical durability. Manufactured through advanced processing techniques, these plates offer optimized heat insulation, excellent oxidation resistance, and extended lifespan. They are widely used in metallurgical processes, chemical reactors, aerospace applications, and industrial furnace systems, providing reliable protection against extreme temperatures and harsh environments.
Product Overview
Graphite protective plates are manufactured from high-purity graphite material through precise processing, designed for use in high-temperature, high-pressure, and highly corrosive environments. Their excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and thermal shock makes them ideal for protection and isolation purposes. These plates provide effective protection against external factors such as high temperatures, corrosion, and wear, enhancing equipment lifespan and operational efficiency.
Key Features
- High-Temperature Resistance: Exceptional stability under extreme temperatures, allowing long-term use in high-heat environments.
- Corrosion Resistance: Graphite's excellent resistance to chemical corrosion enables it to withstand acids, alkalis, and other aggressive substances.
- Thermal Shock Resistance: Maintains performance even in environments with rapid temperature fluctuations, preventing equipment damage.
- High Strength: Offers high compressive strength, capable of withstanding significant external pressure.
- Lightweight Design: Lighter than metal materials, graphite protective plates are easier to install and handle.
- Excellent Thermal Insulation: Low thermal conductivity ensures effective insulation, reducing energy consumption and improving thermal management.
Applications
- Metallurgical Industry: Used for protecting high-temperature furnaces, steel smelting, and other high-heat processing equipment.
- Chemical Engineering: Widely applied in chemical reactors, pipelines, and other equipment, protecting against chemical corrosion and wear.
- Casting Industry: Provides protection in high-temperature casting furnaces, preventing damage from molten metals.
- Energy Sector: Protects high-temperature equipment like gas turbines, boilers, and nuclear reactors, enhancing durability and performance.
- Electronics Industry: Ensures the safe operation of sensitive electronic components during high-temperature manufacturing processes.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Applied in spacecraft, rockets, and other high-pressure, high-temperature environments as a protective material.
 new material
new material