Calcium fluoride double-convex lens is a precision optical component designed for efficient light convergence, minimized spherical aberration, and superior ultraviolet and infrared transmission. Manufactured from high-purity CaF₂, it offers exceptional optical clarity, strong resistance to environmental degradation, and excellent thermal stability. This lens is widely used in laser systems, spectroscopy, aerospace applications, and scientific instrumentation, ensuring optimal light manipulation and performance for advanced optical systems.
Product Overview
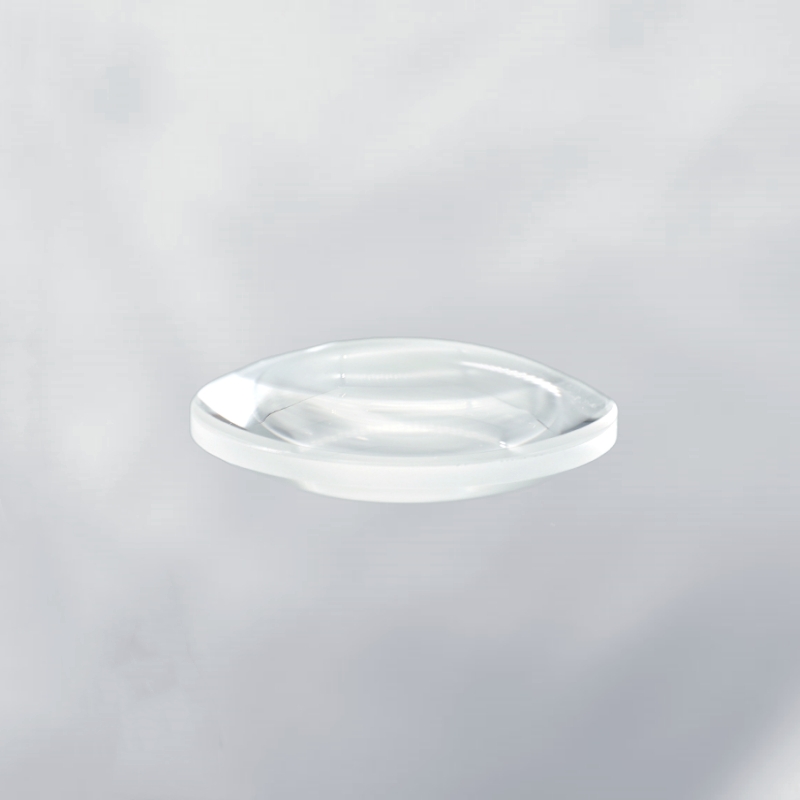
The calcium fluoride double-convex lens is an optical element made from calcium fluoride material, designed with two convex surfaces. It offers a broad transmission spectrum (from 180nm to 8.0μm) and features high damage threshold, low fluorescence, and high uniformity. Due to the relatively soft physical properties of calcium fluoride, the lens surface is more prone to scratching, so care should be taken during handling. Calcium fluoride double-convex lenses are commonly used for collimating laser beams and serve as substrates for various optical elements. The double-convex design, with equal radii on both convex surfaces, focuses light to a single point with a positive focal length, making it ideal for imaging relay systems and object imaging at finite conjugate distances.
Key Features
- Wide Transmission Spectrum: Suitable for a wide range of optical applications, with transmission from 180nm to 8.0μm.
- High Damage Threshold: Exhibits good resistance to laser damage, making it suitable for high-power laser systems.
- Low Fluorescence: Reduces light loss and ensures high transmission and imaging quality.
- High Uniformity: Excellent optical uniformity, ensuring stable imaging performance.
- Physical Properties: While calcium fluoride is relatively soft, its optical performance and chemical stability make it essential in high-end optical applications.
Applications
- Laser Systems: Used for collimating laser beams, improving beam quality and precision.
- Optical Instruments: Applied in devices such as spectrometers and microscopes for precise light focusing.
- Imaging Systems: Ideal for relay systems and object imaging at finite conjugate distances, enhancing image quality.
- High-Power Laser Applications: With its high damage threshold, it is widely used in high-energy lasers and LiDAR systems.
- Optical Element Substrate: Used as a substrate for various optical devices, supporting different optical systems.
| Optical Property | Value |
| Transmission Range | 0.13-10 μm |
| Transmittance | >94%@193nm-7.87μm |
| Refractive Index | 1.4288@2.5μm, 1.39908@5μm |
| Reflection Loss | 5.4%@5μm (both surfaces) |
| Absorption Coefficient | 7.8×10⁻⁴@2.7μm |
| Structure | Cubic Crystal System |
| Cleavage Planes | <111 |
| Physical Property | Value |
| Density | 3.18 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1420 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 9.71 W/(m·K) @ 293K |
| Thermal Expansion | 18.5×10⁻⁶/K @ 273K |
| Knoop Hardness | 158.3 kg/mm² |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 854 J/(kg·K) |
| Dielectric Constant | 6.76 @ 1 MHz |
| Young's Modulus | 75.8 GPa |
| Shear Modulus | 33.77 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | 82.71 GPa |
| Poisson's Coefficient | 0.26 |
| Chemical Property | Value |
| Solubility | 0.016 g/L @ 20℃ |
| Molecular Weight | 78.0748 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
| Diameter Range | 2-300mm |
| Focal Length | 15-5000mm |
| Thickness | 0.12-60mm |
| Surface Quality | 80-50, 60-40, 40-20, 20-10, 10-5 |
| Surface Flatness | λ/2, λ/4, λ/8, λ/10 |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Coating | Customizable |
Submit Your RequirementsWe will contact you within 24 hours.
 WOBO Scientific Research New Materials One-Stop Service Platform
WOBO Scientific Research New Materials One-Stop Service Platform